fabricating metal organic frameworks Metal-organic framework (MOF)-based membranes, featuring potential molecular sieving effects and therefore capable of surmounting the ubiquitous trade-off between membrane selectivity and permeability, hold . $68.99
0 · www.moe.gov.my
1 · the chemistry and applications of metal organic frameworks
2 · metal organic framework synthesis
3 · metal organic framework pdf
4 · metal organic framework overview
5 · metal organic framework materials
6 · metal organic framework images
7 · a review on metal organic frameworks synthesis and applications
Kino vacuum lifters is suitable for sheet metal, stainless steel, aluminum and non-ferrous materials, which is equipped with a series of vacuum monitoring systems to ensure maximum safety. The sucker unit of the Kino vacuum lifter has a .
Metal–organic frameworks (MOFs) have drawn intensive attention as a class of highly porous, crystalline materials with significant potential in various applications due to their .
Metal–organic frameworks (MOFs), known for their versatile structures and high porosity, have become a key focus in materials science with broad applications across multiple . Metal-organic framework (MOF)-based membranes, featuring potential molecular sieving effects and therefore capable of surmounting the ubiquitous trade-off between membrane selectivity and permeability, hold . This study presents a nonalkaline, water-based, and scalable synthesis strategy designed to adjust the water sorption properties of aluminum-based MOFs (Al-MOFs), .
Metal–organic frameworks (MOFs), constructed by organic linkers and metal nodes, are a new class of crystalline porous materials with significant application potentials. Metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) have shown promising potential in water harvesting, but the water uptake of single-component MOFs remains limited. Here, authors .Metal-organic framework (MOF) membranes are attractive for a variety of industrial separation applications. Fabrication of crack/void-free MOF layers that bind tightly to the porous supports .Metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) are emerging porous organic–inorganic hybrid materials composed of metal centers/clusters and various organic ligands, which are widely used in .
Based on the experimentally reported stable and conductive two-dimensional covalent organic frameworks with copper phthalocyanine (CuPc) as building block and cyan . Purifying methane (CH4) from natural gas and coal mine methane (CMM) is of great significance but challenging in the chemical industry. Herein, a robust ultramicroporous metal‐organic framework .Fabricating better metal-organic frameworks separators for Li–S batteries: Pore sizes effects inspired channel modification strategy. / Chang, Zhi; Qiao, Yu; Wang, Jie et al. In: Energy Storage Materials, Vol. 25, 03.2020, p. 164-171. Research output: Contribution to journal › .
Metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) are utilized to integrate with TiO 2 to enhance the solar-to-electricity conversion efficiency. The porphyrin-based MOF PCN-222 is the focus of the study. The MOF/TiO 2 composite is deposited on a flexible ITO-PEN (polyethylene naphthalate) substrate under low-temperature (<150 °C) conditions. The resulting flexible DSSC demonstrates faster . Metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) have gained tremendous popularity in recent years owning to their high surface areas, regular pore sizes, and chemical tunability [1, 2].The fabrication of MOFs membranes and films is an emerging field and has attracted attentions due to their versatile applications in separation, controlled release, sensors, catalysis, proton . Most of the MOFs are electrically neutral as the positive-charged metal ions are neutralized by the negative-charged organic linkers [36].However, there are some cases of ionic MOFs (iMOFs) of which the frameworks are cationic or anionic with counterions in the channels [37].IMOFs result from the mischarged net charge of the skeleton, which needs extra charged . Metal–organic frameworks (MOFs) have drawn intensive attention as a class of highly porous, crystalline materials with significant potential in various applications due to their tunable porosity, large internal surface areas, and high crystallinity. This paper comprehensively reviews the fabrication methods of pure MOF membranes and films, including in situ .
Among the developed MOFs, Hofmann-type MOFs, synthesized from divalent metal ions (such as Co 2+, Ni 2+, Fe 2+), cyanometallate ligands (such as [Ni(CN) 4] 2-) and bidentate organic ligands (such as bipyridine and pyrazine), have attracted great attention for various applications [33, 34].This kind of MOF with abundant oppositely adjacent open metal sites (OMSs) and .
Metal–organic frameworks (MOFs) are porous crystalline materials composed of metallic nodes and organic ligands, demonstrating increasing potential in water harvesting in arid and semiarid regions. This study presents a nonalkaline, water-based, and scalable synthesis strategy designed to adjust the water sorption properties of aluminum-based MOFs (Al-MOFs), . Designing recyclable photocatalysts with high activity and stability has drawn considerable attention in the fields of sewage treatment. Herein, a series of heterojunctions constructed by zirconium-based metal–organic frameworks (UiO-66-NH 2) and tungsten trioxide (WO 3) is immobilized on carbon cloth via a facile solvothermal method, resulting in highly . Stimulus-responsive metal–organic frameworks (MOFs) are compelling candidates for the active components of sensors, actuators, low-power electronics, and energy conversion platforms. However, strategies to precisely integrate single MOF crystals into devices, a crucial condition for fully exploiting their potential in high-performance and energy applications, are .
www.moe.gov.my
Metal–organic frameworks (MOFs) are an emerging class of porous materials constructed from coordination bonding connections between metal ions/clusters and multidentate organic linkers, featuring high porosity, high surface . We have developed a rapid and convenient method for fabricating metal–organic framework (MOF) and infinite coordination polymer (ICP) nanosheets by spraying the atomized solution of metal ions onto the organic ligand solution. Nanosheet formation could be attributed to the anisotropic diffusion of metal ions in the ligand solution, which may give rise to a lateral .
Developing an efficient, environmentally friendly, and pollution-free catalyst with excellent visible light catalytic activity is a promising strategy for dye wastewater treatment. Herein, the rod-like hollow BiOClxBr1−x (x=1, 0.75, 0.5, 0.25, 0), with an adjustable band gap, was successfully prepared using Bi-based metal-organic framework as template. The .
Tunable Cu-BTC mesoporous metal–organic frameworks (mesoMOFs) are prepared conveniently through a template-free strategy under solvothermal conditions. Nanosized microporous Cu-BTC particles pack to form mesopores with sizes that can be controlled (26–72 nm) by simply varying the synthesis temperature. This template-free and controllable strategy . Energetic materials have been widely applied in civil and military fields, whose thermostability is a key indicator to evaluate their safety levels under severe conditions. Herein, two novel energetic metal–organic frameworks . Porous metal-organic frameworks (MOFs), formed from organic linkers and metal nodes, offer advantages in sensitive and selective analyte recognition through precisely tuned pore environments and molecular sieving. . Another approach involves the fabrication of a hierarchical pore architecture for fast sensing of NO 2 (Figure 10 E). 96 This .
Metal–organic frameworks (MOFs), also known as porous coordination polymers (PCPs), are constructed by organic linkers and metal ions or clusters and have emerged as a new type of crystalline materials with large surface area (typically ranging from 1000 to 10,000 m 2 /g), high porosity, tunable structures, and flexible tailorability, compared with traditional porous .Fabrication of metal‐organic frameworks macro-structures for adsorption applications in water treatment: A review. Author links open overlay panel Xiaoqin Yang a b 1, . Metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) are emerging porous organic–inorganic hybrid materials composed of metal centers/clusters and various organic ligands, which are widely . Currently, other fabrication methods for MOF membranes, including layer-by-layer techniques, interfacial growth and current-driven growth, have been reported. . Fabrication of oriented metal-organic framework nanosheet membrane coated stainless steel meshes for highly efficient oil/water separation. Sep. Purif. Technol., 229 (2019), p.
Herein, a rapid and efficient synthesis of MOF/aerogel composites via a spray strategy is presented in this work. In brief, metal ion and organic ligand solutions at a certain ratio are orderly sprayed in the form of droplet on the aerogel, obtained by simple freeze-drying, to prepare the MOF/aerogel composite (Scheme 1).The spray technique is easy scalable, which . Metal–organic frameworks (MOFs), known for their versatile structures and high porosity, have become a key focus in materials science with broad applications across multiple research areas. This review offers a prospective outlook, emphasizing the use of MOF-based ion-selective nanofluidic membranes in critical areas such as ion separation, seawater . Metal-organic framework (MOF)/polymer composites have attracted extensive attention in the recent years. However, it still remains challenging to efficiently and effectively fabricate these composite materials. In this study, we propose a facile one-pot electrospinning strategy for preparation of HKUST-1/polyacrylonitrile (PAN) nanofibrous membranes from a . Metal organic frameworks are a group of extended crystalline nanomaterials assembled from metal clusters and organic ligands to form one-, two-, or three-dimensional structures, which may have interesting functional properties [23, 24].In 3D MOF structures, their inherent compositional arrangement confers MOFs with enduring porosity, modifiable pore .
Development of metal-organic framework (MOF) films is of great importance to expand their applications. Herein, we report a facile and universal method of liquid-phase epitaxial (LPE) layer by layer (LBL) brushing approach for fabricating MOF films on various substrates in a high-throughput fashion. This MOF films preparation method offers a great prospective to cost .
the chemistry and applications of metal organic frameworks
whitley service roofing & sheet metal company
Metal–organic frameworks (MOFs) are an emerging class of porous materials composed of organic linkers and metal centers/clusters. The integration of MOFs onto the solid surface as thin films/coatings has spurred great interest, thanks to leveraging control over their morphology (such as size- and shape-regulated crystals) and orientation, flexible .
Metal-organic framework (MOF) membranes are attractive for a variety of industrial separation applications. Fabrication of crack/void-free MOF layers that bind tightly to the porous supports is one of the preconditions to achieve optimal performance of MOF membranes. Because of their diverse structure, high porosity, and tunable functionality, metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) are of great interest for diverse applications, including catalysis. However, the poor hydrostability of most reported MOFs hinders their catalytic applications seriously. In addition, the d .

white vintage metal wall art on house exterior
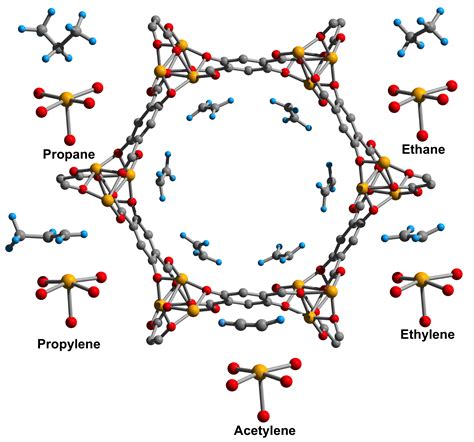
metal organic framework synthesis
Ask This Old House master electrician Heath Eastman explains the uses and purposes of different types of electrical boxes. Selecting the right electrical box for your project can be confusing because of the many options available.
fabricating metal organic frameworks|metal organic framework pdf